My Health Blog
Health, Fitness, Ultrasound, Radiology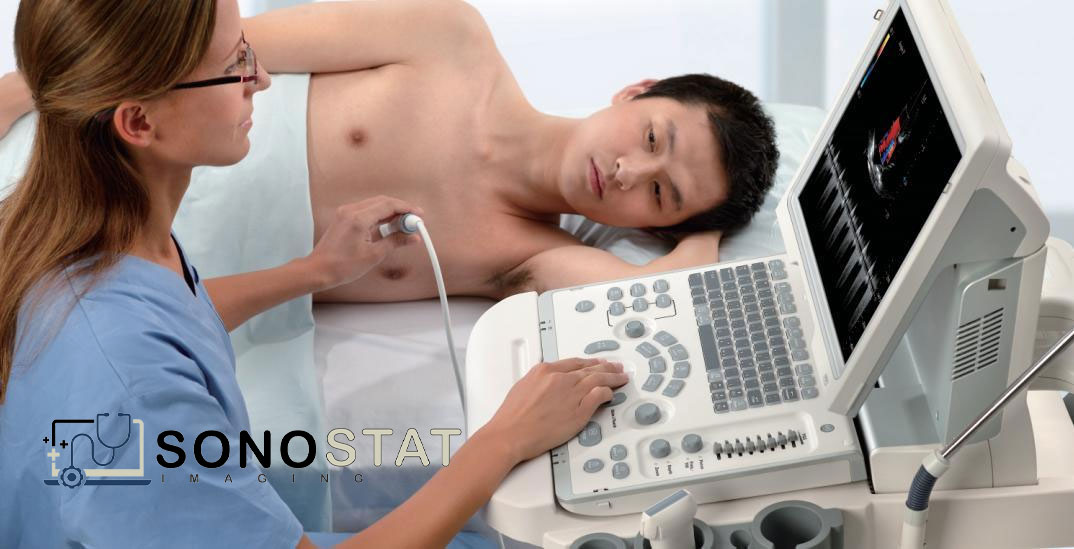
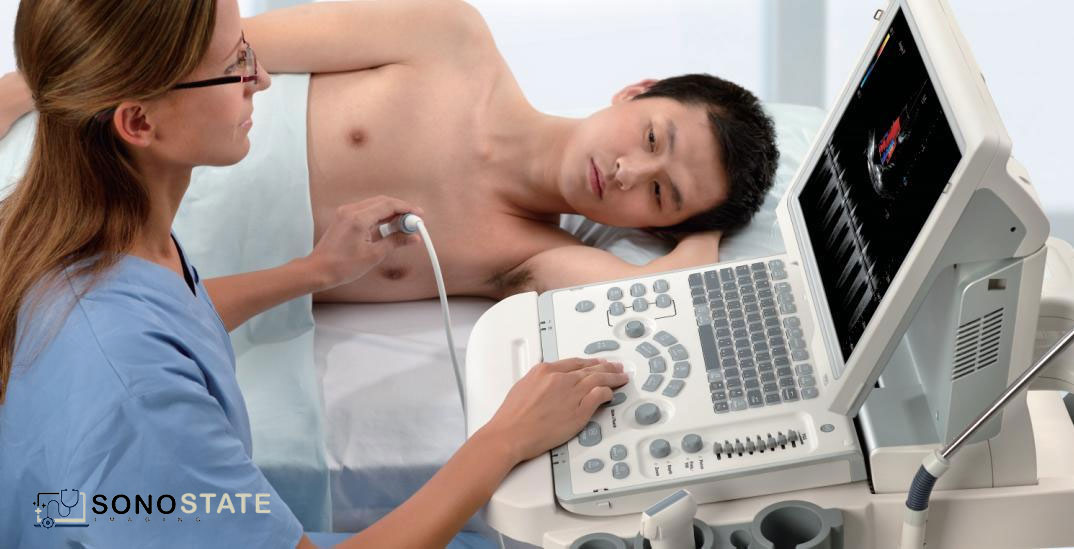
Mobile Ultrasound
Introduction: In the realm of medical diagnostics, one technology stands out for its versatility, safety, and effectiveness—ultrasound. Utilizing sound waves to create images of internal body structures, ultrasound has become an indispensable tool for healthcare professionals across various specialties. From obstetrics to cardiology, the applications of ultrasound are vast and continue to expand, shaping the future of medical imaging. In this article, we delve into the fascinating world of ultrasound and explore its benefits, advancements, and potential.
The Basics of Ultrasound: Ultrasound, also known as sonography, is a non-invasive imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to capture real-time images of organs, tissues, and blood flow within the body. The process involves a transducer, which emits sound waves, and a computer that analyzes the returning sound waves to generate images on a screen. Unlike other imaging methods, such as X-rays or CT scans, ultrasound does not utilize ionizing radiation, making it safe for patients of all ages, including pregnant women.
Key Applications:
- Obstetrics and Gynecology: One of the most well-known applications of ultrasound is in monitoring fetal development during pregnancy. Obstetric ultrasound enables healthcare providers to assess the health of the fetus, track growth, detect anomalies, and even determine the baby’s gender. Additionally, gynecologists employ ultrasound to examine the reproductive organs, diagnose conditions like ovarian cysts or fibroids, and guide procedures such as biopsies or intrauterine device (IUD) placement.
- Cardiology: Ultrasound plays a pivotal role in cardiology, facilitating the diagnosis and management of heart conditions. Echocardiography, a specialized form of ultrasound, produces detailed images of the heart’s structure, valves, and blood flow patterns. This technique aids in detecting heart defects, assessing cardiac function, diagnosing heart attacks, and monitoring the effectiveness of treatments such as stent placements or pacemaker implantations.
- Abdominal Imaging: Ultrasound is widely used to evaluate abdominal organs, including the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, kidneys, and spleen. It helps identify abnormalities such as tumors, cysts, or stones, guide biopsies, and assess blood flow to organs. Furthermore, ultrasound-guided procedures, such as needle aspirations or drain placements, are increasingly performed for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
Advancements and Innovations: As technology continues to advance, ultrasound imaging has seen remarkable developments that enhance its diagnostic capabilities. Here are a few notable advancements:
- Portable and Handheld Ultrasound Devices: The advent of portable and handheld ultrasound devices has transformed the accessibility and convenience of ultrasound imaging. These compact devices offer real-time imaging on a mobile platform, enabling healthcare professionals to perform bedside examinations, emergency evaluations, or rural healthcare outreach efficiently.
- Three-Dimensional (3D) and Four-Dimensional (4D) Ultrasound: Traditional ultrasound produces two-dimensional images, but the introduction of 3D and 4D ultrasound has added a new dimension to diagnostics. These techniques provide volumetric images that enhance the visualization of complex structures, aiding in the evaluation of fetal anomalies, assessing cardiac function, and improving preoperative planning.
- Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound: Contrast agents are now utilized in ultrasound to improve visualization of blood flow and enhance the detection of certain abnormalities. By injecting microbubbles into the bloodstream, ultrasound imaging can better assess vascularity in tumors, detect liver lesions, and assess perfusion in organs.